Propagation of Radio Signals Over the Sea Surface
Propagation of radio signals can be significantly affected by the characteristics of the medium in which they travel such that the properties of the propagation path affect both the level and quality of the received signal as well as the distance over which signals can be reliably detected. In addition to factors such as reflection, refraction and diffraction that affect the propagation of a single signal, additional effects may arise from other signals propagating in the vicinity.
Over the past few years, the modeling of radio wave propagation over the sea surface has drawn the attention of many researchers. Channel models have been developed for different frequencies and communication scenarios. There are models that emphasize the influence of the height of the evaporation duct in the marine environment, as well as models that deal with different frequencies or the impact of various parameters, such as transmitter antenna height and wave height.
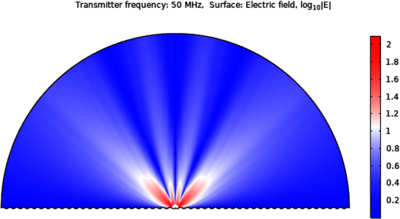
This work is focused on analyzing the propagation of a radio signals along the Line-of-Sight (LoS) between a transmitter that remains close to the sea surface and a receiver located on a ship some distance away. To accurately calculate the propagation loss, reflection and diffraction effects of the propagating electromagnetic wave due to the sea surface must be accounted for. A model has been developed using the RF module in COMSOL Multiphysics® simulation software, based on solving the full Maxwell wave equation and calculating the propagation loss over large distances, up to ten kilometers. The model accurately accounts for a variety of effects such as: transmitter frequency, wave height and wavelength), transmitter height and its location with respect to the wave trough and crest, and dependence of the electrical conductivity of the sea on temperature and salinity.
Herunterladen
- koppenhoefer_rfoptics_presentation.pdf - 0.82MB
- koppenhoefer_paper.pdf - 0.96MB
