On the influence of some geometric parameters for DAB+ signal’s propagation in tunnels
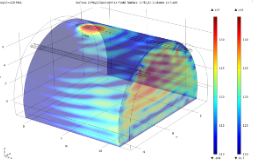
Obtaining a good coverage of Digital Audio Broadcasting (DAB) service, in the 200 MHz band, in motorway tunnels is quite a challenging task. Recently, Rai Research Centre (CRITS) has been involved in investigating alternative (and cheaper) solutions than those adopted so far (radiating cables i.e. “leaky-feeders” installed along the tunnel ceiling). In [1] the “direct RF radiation” approach, consisting of antennas positioned near gallery’s entrance, either internally or just outside it, has been analyzed numerically, using a Finite Element (FEM) simulative solution employing COMSOL Multiphysics and LiveLink™ for MATLAB® module. Such simulative results have also been compared with test measurements performed on the fields. Interesting highlights have been found in terms of field’s attenuation as a function of distance for different radii of curvature, as well as the type of polarization supported. To this end, the anti-intuitive result was verified, already resulting from field tests [2], that the best coverage in terms of distance in the tunnel is obtained by transmitting in horizontal polarization (H-Pol), although the receiving antenna has vertical polarization (V-Pol). Furthermore, the study of the signal attenuation with distance has shown that the exact identification of electromagnetic parameters of the materials that constitute the vault and the road pavement (namely, the dielectric permittivity and the conductivity) does not play a fundamental role, while the geometric parameters of the tunnel have a very strong impact. Among them, the section geometry has a direct effect on the signal attenuation, that can be easily studied by means of mode analysis [1]. In order to further investigate the impact of the curvature radius of a tunnel section and the incidence angle of the wave front entering the gallery, in the present work the power flows passing through the transverse sections at progressive distances from the entrance and those that leak below the road surface and beyond the surface of the vault have been analysed. These quantities allow us to investigate the "energy dynamics" of the system: the input power is partly reflected by the lateral surfaces - vault and road surface - and therefore propagated towards the exit, and partly leaks through the vault and road surface and is therefore lost in thermal dissipation in the material. The percentages of transmission or reflection depend (also) on the angle with which the wave impacts on the surfaces, and therefore on the two parameters considered in this paper. The final effect is the greater or lesser attenuation suffered by the signal that reaches the remote end of the tunnel. Finally, interesting results have been obtained for different types of illumination used with internal or external antenna (an example with the antenna placed on the vault is reported in Figure 1). The investigation of all the most relevant and critical aspects of DAB+ signal propagation inside tunnels by means of a simulative approach (confirmed by fields test measurements) have led to the set-up of a tool that can be applicable to every type of tunnel’s configuration for the verification and optimization of local transmission installations in such challenging scenarios.
Herunterladen
- devita_8781_poster.pdf - 0.93MB
