Amphos 21 Consulting

Address & Contact Information
Headquartered in Barcelona, Spain, we have offices in Chile and Peru.
Headquarters - Spain
Amphos 21 Consulting S.L., España
C/ Veneçuela, 103, 2nd Floor
08019, BARCELONA, Spain
Tel: +34 93 583 05 00
Email: amphos21@amphos21.com
Amphos 21 Consulting Chile Ltda.
Av. Nueva Tajamar, 481, of. 1005 (Torre Sur)
Las Condes 7550099, SANTIAGO DE CHILE, Chile
Tel: +562 27991630
Email: amphos21chile@amphos21.com
Amphos 21 Consulting Perú S.A.C.
Jr. Pietro Torrigiano, 396
LIMA 41, Peru
Tel: +511 592-1275
Email: amphos21peru@amphos21.com
Amphos 21 has offered scientific, technical, and strategic environmental consulting services since 1994. Our multidisciplinary team provides solutions in the fields of chemistry, biogeochemistry, geosciences, and engineering. We serve various industries, including surface and geological disposal of radioactive waste, mining, oil & gas, water resources management, circular economy, and industrial processes.
Areas of Expertise
- Groundwater flow in porous and fractured media
- Contaminant reactive transport
- Multiphase flow and heat transfer in porous and fractured media
- Geomechanics of natural systems and nonlinear solid mechanics of construction materials
- Coupling state-of-the-art geochemical models with multiphysics
- Coupling of thermo-hydro-chemo-mechanical processes
- Computational fluid dynamics
- Tailor-made physics user interfaces and apps in COMSOL®
- Development of reactive transport models using interface COMSOL® PHREEQC (iCP)
- Customized training courses in modelling, geosciences, and chemistry
Featured Projects Using COMSOL Multiphysics®
The following are some examples of our work using COMSOL Multiphysics®:
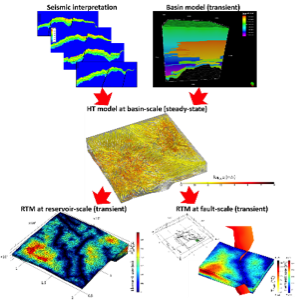
Thermo-Hydro-Chemical Assessment of Dolomitization for the O&G Industry: Basin-Scale Study
Numerical study using 3D reactive transport modeling of porosity evolution in a carbonate reservoir through dolomitization. The model is based on a currently producing carbonate reservoir with large regions of high porosity values deduced through seismic inversion. Using an embedded model approach, the geochemical reactions in the reservoir have been coupled to the thermo-hydrogeological behavior of the entire basin.
|
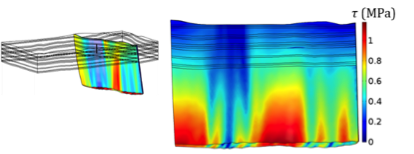
Multiphase Reactive Transport and Geomechanics of the Injection of CO2 for Carbon Capture and Storage
A planned in situ experiment for CO2 injection into a shallow fault was simulated using multiphase flow models and explicitly accounting for chemical reactions between injected gas and the carbonate system and for the geomechanical impact of the injection process.
 |
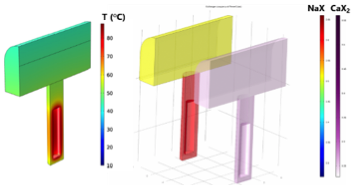
Thermo-Hydro-Geochemical Evolution of a Bentonite Barrier for Spent Fuel Disposal in Granitic Rock
The geochemical evolution of bentonite barriers for spent fuel disposal during the transient thermal period was simulated with iCP, an interface between COMSOL® and PHREEQC. The model included thermo-hydro-geochemical coupled processes during the saturation of the barrier with groundwater while heat is released from the waste contained in a copper canister.
 |
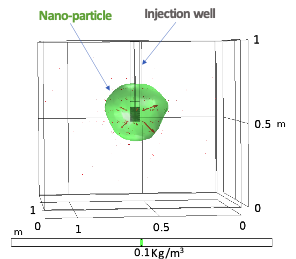
Particle Transport Modeling to Study the Fate of Nanoparticles in the Subsurface
Nanoparticles injection in subsurface has emerged as a novel technique for contaminated groundwater remediation. The fate of these particles in the subsurface was predicted by developing a particle transport model in COMSOL®. Predictions were made of the concentration of ZVI nano-particles after injection into an aquifer with sand layers with a range of permeabilities.
 |
Hydro-Chemo-Mechanical Processes in the Mining Industry
Heap leaching, a metallurgical process to extract metals from ore recovered from underground mines, was modeled with COMSOL®. The model was based on soil mechanics and explicitly included the impact of groundwater flow and mineralogical reactions on the dynamics of the system.
|
Modeling Pollutant Transport in a Discrete Fractured Media
3D modeling of the transport of a dissolved radionuclide in a fractured media represented as a set of hundreds of 2D planar surfaces with different lengths and orientations. The model accounts for convection, diffusion, and retention processes such as sorption, chemical reactions, and radioactive decay.
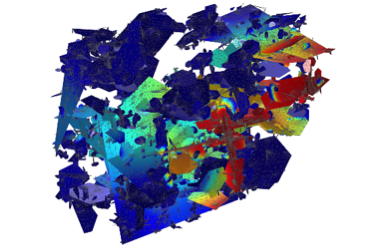
|
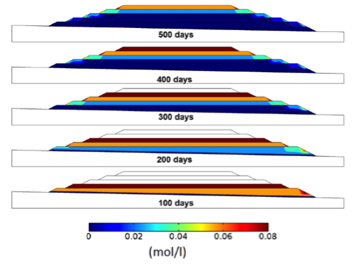
Modeling Radionuclide Transport and Retention in the Near-Surface
Basin-scale groundwater flow and radionuclide transport modeling to understand preferential paths and accumulation patterns of radionuclides in loose quaternary sedimentary materials. The model accounts for chemical reactions and radioactive decay.
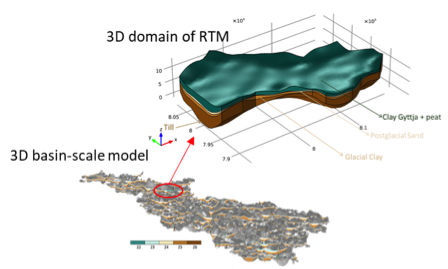
|
Hydro-Chemo-Mechanical Study of the Durability of Concrete Structures
Quantitative assessment of concrete durability of the underground structures for disposal of low- and intermediate-level waste in Sweden. The study focused on the long-term hydro-chemical processes and their potential impact on the mechanical stability of the concrete structures.
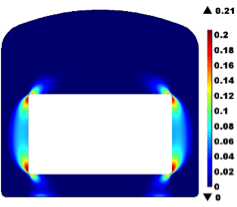
|
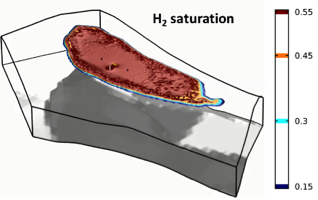
Studies on the Dynamics of Carbon Dioxide and Hydrogen in Underground Gas Storage
The injection, migration, retention, and fate of gases in subsurface gas storages are assessed through miscible 3D multiphase flow models for energy (short-term) and carbon capture (long-term) projects.
|
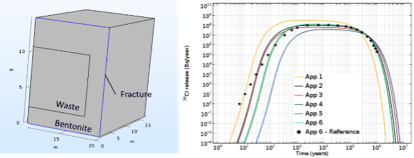
Radionuclide Diffusive Transport Through Bentonite Barriers and Decay
The flux of an anionic radionuclide, Cl36, escaping a bentonite barrier of a repository vault for future disposal of long-lived low- and intermediate-level waste, was quantified by means of five different diffusion models of anionic species through compacted bentonite in COMSOL®.
|
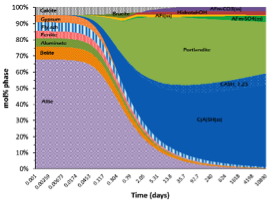
Hydro-Chemical and Thermodynamic Modeling of Cement Hydration and Long-Term Concrete Degradation in Underground Structures
Assessment of the effect of different cement types and concrete mixes on the long-term performance of a repository vault of the future SFL repository by means of reactive transport simulations and thermodynamic modeling of the hydration of the different systems.
|
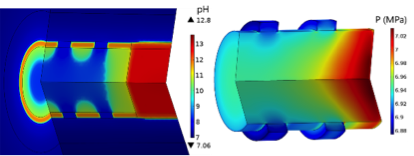
Hydro-Chemo-Mechanical Modeling of Swelling Clays for Closure of Nuclear Waste Repositories
Coupled hydro-mechanical-chemical numerical modeling to simulate the long-term behavior and performance assessment of closure systems of the future geological disposal facility Cigéo for radioactive waste disposal in France.
|
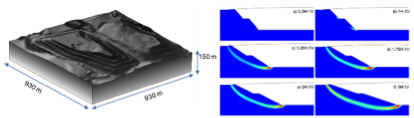
Geomechanics of Landfill Mining
Elastoplastic models coupled to fluid flow were used to assess the potential of a mining operation in an existing landfill of municipal solid waste. All available data regarding the hydraulics of the system and geomechanical tests were integrated in the model.
|
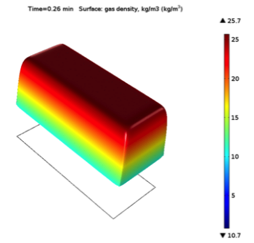
Multicomponent Gas Flow in Shale for the O&G Industry
COMSOL® was used to simulate multicomponent gas flow in shale, a porous media with extremely small pore size. Several transport processes were considered, such as Knudsen diffusion and solution gas to study gas behavior in shale samples under well-controlled experimental conditions.
|
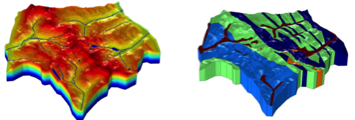
Groundwater Flow Modeling as a Management Tool for Underground Mines in Fractured Massifs
Metallic ores mines in heterogeneous fractured massifs can impact the streams and lakes and change the natural water balance. Quantification of these impacts by 3D modeling of fractured porous media was performed to assess the sustainability of the construction and operation periods.
|
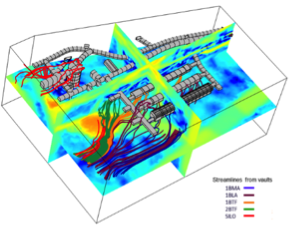
Groundwater Flow Modeling for Optimization of Engineered Barriers for Radioactive Waste Underground Disposal
The future hydraulic behavior of the SFR repository in Sweden under saturated and steady-state conditions was studied to determine flow values used as input to radionuclide transport calculations.
|
Consultant Contributions
Amphos 21 has contributed to the COMSOL conferences with more than 40 publications since 2012, either as posters or oral presentations. We have also given several webinars and training courses. We developed iCP, an interface between COMSOL® and the geochemical simulator PHREEQC to couple multiphysics with state-of-the-art geochemistry (click here for more information).
